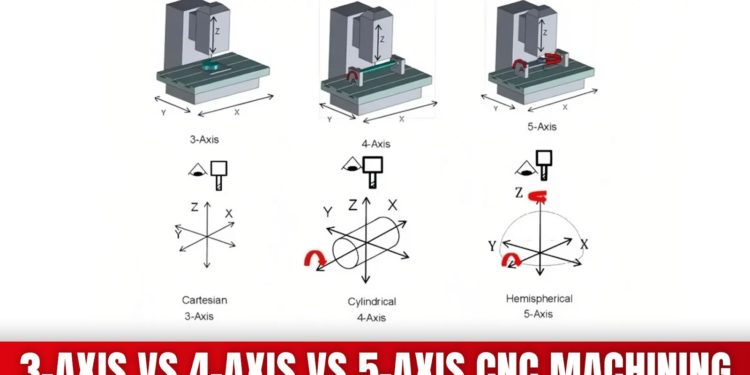
Ever wondered how many axes on a CNC machine affect the parts you make? The more axes the machine has, the more complex and detailed the parts can be.
A 3-axis CNC machine moves in three straight lines—left to right, front to back, and up and down. Good for simple, flat parts. A 4-axis machine adds rotation, which helps cut different sides of a part without stopping the machine. A 5-axis machine has the most movement. It can cut from almost any angle, perfect for detailed and curved designs.
Anyone making parts—simple or complex—choosing the right CNC machine is key. That’s why many companies work with skilled machining teams like ProleanTech that offer different CNC options to fit their needs.
In this article, we’ll break down the main differences between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining and how choosing the right one will help with your design, budget and production goals.
What is CNC Machining?
First, we need to know what CNC machining means. Then we can look at different types of axes.
CNC machining uses computers to control cutting machines. The computer tells the machine exactly what to do. The machine cuts and shapes materials into final parts. This method takes away material from a big block. The machine removes parts until the right shape forms.
CNC machines work very well and make few mistakes. They can cut many different types of materials easily. The machines cut metal, plastic, and composites with great success.
The word “axis” means a direction of movement here. The tool can move in this direction during cutting. The material can also move in this direction sometimes.
More axes means the machine can make harder parts. The machine does not need to stop and change setup.
Undersatnding 3-Axis CNC Machining
3 axis CNC machining is the most common and simple form of CNC machining.
How It Works:
- The machine moves the cutting tool along three straight lines: X (left to right), Y (front to back), and Z (up and down).
- The part stays still while the cutting tool does all the moving.
Key Benefits:
- Good for basic shapes
- Cheap and easy to find
- Works well for most common parts like brackets, plates, and housings
Limitations:
- Does not work well for undercuts or hard curves
- Needs manual moving for some angles
Best for: Flat or shallow parts, starter prototyping, and low to medium hard designs.
Understanding 4-Axis CNC Machining
4 axis machining adds one spin axis to the basic three axes.
How It Works:
- The machine moves in X, Y, and Z directions like before. The part or tool also spins around one axis now. This spin usually happens around the X-axis direction.
- This extra spin lets the machine cut the sides of parts. The machine does not need manual moving of the part.
Key Benefits:
- The machine can cut on many sides of parts
- This works better for round or spiral shaped parts
- Less human help is needed for setup and work
Limitations:
- This still does not work well for complex 3D shapes. Deep holes and cavities are still hard to make.
- The cost is a bit higher than 3-axis machines
Best for: Turbine parts, camshafts, gear wheels, and jobs that need cutting around round objects.
Understanding 5-Axis CNC Machining
5 axis CNC machining adds two turning movements to three straight movements. These turning movements can go around X axis, Y axis, or Z axis. This depends on how the machine is built.
How It Works:
- The cutting tool or part can move and turn at the same time across five different directions.
- This multi axis milling machine allows full shaping, drilling, and complex cutting in one single setup.
Key Benefits:
- Reaches almost any angle and surface in one operation
- Removes the need for many different setups
- Gives perfect accuracy and smooth surface finish
- Works great for complex parts with deep holes and detailed shapes
Limitations:
- Costs more money for machine and daily operations
- Needs skilled programming knowledge and training
- May not be needed for simple and basic parts
Best for: Airplane parts, medical tools, car parts, and complex mold making.
3-Axis vs 4-Axis CNC: Which One Do You Need?
Your production makes simple parts with flat surfaces. These parts have no curved features at all. 3-axis CNC machining works well for this job. It costs less money than other options. Small businesses can buy these machines easily. Startups can afford them without big problems.
Your parts need machining on many different sides. Some parts have circular features that need work. 4-axis CNC machining works much better for this. It saves time on manual setup work. It makes parts more accurate on all faces.
| Feature | 3-Axis CNC | 4-Axis CNC |
| Movement | X, Y, Z | X, Y, Z + rotation |
| Setup Time | Higher | Lower |
| Suitable For | Simple parts | Cylindrical or multi-face parts |
| Cost | Lower | Moderate |
3-Axis vs 5-Axis CNC: Is It Worth the Investment?
You compare 3-axis machines to 5-axis CNC machines. The difference between them is very big. A 5-axis machine gives you more flexibility. It performs better than other machines do. But it costs much more money to buy. The programming is harder to learn and use.
Your business makes parts with complex shapes inside. These parts have deep holes and tight spaces. The tolerances must be very exact and precise.
The investment in 5-axis machines pays off well. Standard jobs work fine with 3-axis machines. These machines give good precision at lower cost. Here is the quick difference table for 5 axis vs 3 axis cnc:
| Feature | 3-Axis CNC | 5-Axis CNC |
| Movement | X, Y, Z | X, Y, Z + 2 rotation axes |
| Setup Time | High | Minimal |
| Complexity Handling | Low | Very High |
| Suitable For | Basic geometries | Complex parts & multi-face machining |
| Cost | Lower | High |
4-Axis vs 5-Axis CNC: Which to Choose?
Both 4-axis and 5-axis CNC machines rotate parts. But they rotate parts in different ways completely.
4-axis machines work well for most basic jobs. The added complexity of 5-axis is not needed. You do not work with detailed 3D surfaces. You do not make parts with intricate angles. 4-axis gives you an excellent balance here. It balances cost and capability very well together.
Choose 5-axis CNC only when your part needs it. Your part geometry must justify this big expense. Complex aerospace brackets need this advanced machine type.
Medical implants require this level of precision too. High-precision components with internal features work best here. These examples show where 5-axis machines really shine.
| Feature | 4-Axis CNC | 5-Axis CNC |
| Rotational Axes | 1 | 2 |
| Ideal for | Side machining | Complex contours |
| Precision | High | Very High |
| Setup Time | Moderate | Minimal |
| Cost | Medium | High |
Quick Comparison Table – 3 Axis vs 4 Axis vs 5 Axis CNC
CNC machines have different types based on movement directions. Each extra direction gives more ways to make detailed parts. Here are the three most common types:
| Feature | 3-Axis CNC | 4-Axis CNC | 5-Axis CNC |
| Movement Directions | X, Y, Z | X, Y, Z + 1 rotation axis | X, Y, Z + 2 rotation axes |
| Complexity Level | Basic | Moderate | Advanced |
| Setup Changes | Manual reposition | Fewer reposition steps | No repositioning needed |
| Best For | Flat parts | Round/angled parts | Complex 3D or curved surfaces |
| Cost | Low | Medium | High |
Types of CNC Milling Machines
Different CNC milling machines work for different jobs. Here are the main types:
Vertical Milling Machine
- The cutting tool goes up and down.
- This type is most common and easy to use.
- It works best for basic parts and simple cutting.
Horizontal Milling Machine
- The tool moves side to side across the part.
- This machine works well for heavy and big parts.
- It removes chips better than vertical machines do.
Gantry (Bridge) Milling Machine
- The part stays still while the tool moves over.
- This machine works great for large and heavy parts.
- Car and airplane makers use this machine often.
Universal Milling Machine
- This machine offers both up-down and side movement.
- It can make many different types of parts.
- Some models support four-direction or five-direction cutting setups.
Multi-Axis CNC Mill
- This machine can have four, five, or more directions.
- It cuts in full 3D from all angles possible.
- Complex designs and tight fits use this machine type.
Conclusion
Choosing 3-axis vs 4-axis vs 5-axis is more than a technical decision—it’s a business decision. Knowing the pros and cons of each axis system means better quality, lower cost and faster turnaround.
3-axis CNC works best for simple flat parts that move in three straight ways. 4-axis CNC adds turning motion so it can work on many sides without stopping the machine. 5-axis CNC gives full freedom to cut hard shapes from almost any angle with very good precision.Proleantech help clients choose the right process based on real needs—not hype. Not sure which machining solution is right for your next project? Contact ProleanTech today to get CNC Milling Services.
FAQs
Q1: What is 5-axis CNC?
A 5-axis CNC machine moves in three straight ways and also turns in two ways. This lets it cut hard shapes from many angles without stopping at all.
Q2: What is the difference between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC?
- 3-axis moves in three ways which are X, Y, and Z directions.
- 4-axis adds turning motion for cutting on more sides of the part.
- 5-axis gives full movement and can cut from almost any angle possible.
Q3: What are the disadvantages of 5-axis machining?
5-axis machines cost more money and need skilled people to run them well. The programming work is also much harder compared to 3-axis or 4-axis machines.
Q4: What is a 5-axis CNC machine used for?
It makes very detailed parts with curves or hard shapes like those in airplane parts, medical parts, or car parts.
Q5: What are the limitations of 4-axis CNC?
4-axis machines cannot reach all angles like 5-axis machines can do well. They do not work well for very hard or deep 3D shapes.
Q6: What is a 3-axis CNC machine used for?
It makes basic parts with flat surfaces, slots, holes, and simple cuts only. It works perfect for easy and straightforward jobs that are not complex.
Q7: Which machining process is more accurate?
5-axis machining gives the best accuracy because it can reach tight angles well and reduces the need to move the part between different cuts.







![7 Best POS Software in the UK [2026 Edition]](https://todaynews.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/7-Best-POS-Software-in-the-UK-2026-Edition-360x180.png)