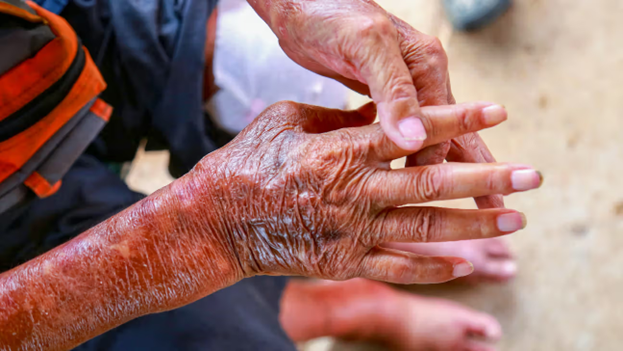
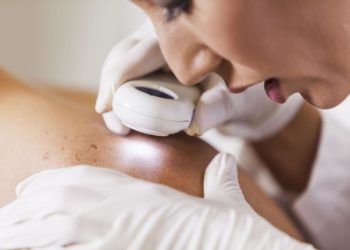
Scleroderma is a serious autoimmune disease, which is rare but severe, and is known to attack the connective tissues of the body. The name is given after Greek words that denote hard skin, which is one of the most striking characteristics. Nevertheless, the skin is not the only area that is afflicted by this condition. In most instances, it may also interfere with internal organs like lungs, heart, kidney and digestive system. Although scleroderma may be difficult to deal with, it can be seen to have a lot better life when diagnosed early and treated properly. This paper describes the scleroderma in details, its causes, symptoms, and step-by-step treatment choices.
What Causes Scleroderma?
The reason behind the scleroderma is not clear yet the medical professionals assume that this disease arises as a result of a complex of immune system dysfunction, genetics, and environmental factors combined.
1. Autoimmune Response
Scleroderma is a condition that is caused when the immune system attacks normal tissues. This causes excess production of collagen, a type of protein that ordinarily assists in supporting the organs and the skin. Overabundance of collagen leads to stiffening of tissues making them thicker and less elastic.
2. Genetic Factors
Scleroderma is not a hereditary disease, but the presence of an autoimmune disease in the family history can predispose the risk. Some genes are capable of rendering an individual susceptible to acquisition of the condition.
3. Environmental Triggers
Even exposure to certain environmental conditions, like silica dust, certain chemicals, or viral infection,s can cause scleroderma in individuals who are already genetically predisposed.
Common Symptoms of Scleroderma
Symptoms of scleroderma can vary widely depending on the type and severity of the disease. Some people experience mild symptoms, while others may face more serious complications.
1. Skin Changes
- Thickened or hardened skin
- Tight or shiny appearance, especially on fingers, hands, and face
- Reduced flexibility and movement
2. Circulation Problems
Many people with scleroderma develop Raynaud’s phenomenon, where fingers and toes turn white or blue in response to cold or stress. This happens due to poor blood flow.
3. Digestive Issues
- Difficulty swallowing
- Acid reflux or heartburn
- Bloating and digestive discomfort
4. Internal Organ Involvement
In more severe cases, scleroderma may affect vital organs, leading to breathing problems, high blood pressure, kidney issues, or heart complications.
Types of Scleroderma?
Scleroderma is available in two major varieties, which have different impacts on the body differently
1. Localized Scleroderma
It does not normally affect internal organs and can be improved with time.
2. Systemic Scleroderma
Systemic scleroderma is more severe, and it may impact the internal organs and the skin. It demands chronic medical services and follow-ups.
Step-by-Step Treatment Options for Scleroderma
Although there is no permanent cure for scleroderma, treatments focus on managing symptoms, slowing disease progression, and preventing complications.
Step 1: Early Diagnosis and Monitoring
Regular checkups and early diagnosis are crucial. Doctors may use blood tests, imaging scans, and physical examinations to monitor disease activity.
Step 2: Medications
- Immunosuppressive drugs to control the immune system
- Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and swelling
- Blood pressure medications to improve circulation
Step 3: Managing Skin and Joint Symptoms
Moisturizers, physical therapy, and gentle stretching exercises help maintain skin flexibility and joint movement.
Step 4: Treating Organ-Related Complications
Specific treatments may be prescribed for lung, heart, kidney, or digestive issues, depending on which organs are affected.
Step 5: Lifestyle Changes and Support
- Avoid cold exposure to reduce circulation problems
- Eat a balanced diet to support digestion
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques
Support groups and counseling can also help patients cope emotionally with the condition.
Final Thoughts:
Scleroderma is a complex and long-term condition, but with early diagnosis, proper medical care, and lifestyle adjustments, many people are able to manage their symptoms effectively. Understanding the causes, recognizing early symptoms, and following a step-by-step treatment plan can make a significant difference in slowing disease progression and improving daily life. Ongoing medical research continues to bring hope for better treatment options in the future. With the right support system, awareness, and consistent care, individuals living with scleroderma can maintain a better quality of life and stay empowered in their health journey.







![7 Best POS Software in the UK [2026 Edition]](https://todaynews.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/7-Best-POS-Software-in-the-UK-2026-Edition-360x180.png)